Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Regularization paths for the Graphical Lasso and its Adaptive variation#
This example demonstrates how non-convex penalties in the Adaptive Graphical Lasso can achieve superior sparsity recovery compared to the standard L1 penalty.
The Adaptive Graphical Lasso uses iterative reweighting to approximate non-convex penalties, following Candès et al. (2007). Non-convex penalties often produce better sparsity patterns by more aggressively shrinking small coefficients while preserving large ones.
- We compare three approaches:
L1: Standard Graphical Lasso with L1 penalty
Log: Adaptive approach with logarithmic penalty
L0.5: Adaptive approach with L0.5 penalty
The plots show normalized mean square error (NMSE) for reconstruction accuracy and F1 score for sparsity pattern recovery across different regularization levels.
# Authors: Can Pouliquen
# Mathurin Massias
# Florian Kozikowski
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import norm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
from skglm.covariance import GraphicalLasso, AdaptiveGraphicalLasso
from skglm.penalties.separable import LogSumPenalty, L0_5
from skglm.utils.data import make_dummy_covariance_data
Generate synthetic sparse precision matrix data#
p = 100
n = 1000
S, _, Theta_true, alpha_max = make_dummy_covariance_data(n, p)
alphas = alpha_max*np.geomspace(1, 1e-4, num=10)
Setup models with different penalty functions#
penalties = ["L1", "Log", "L0.5"]
n_reweights = 5 # Number of adaptive reweighting iterations
models_tol = 1e-4
models = [
# Standard Graphical Lasso with L1 penalty
GraphicalLasso(algo="primal", warm_start=True, tol=models_tol),
# Adaptive Graphical Lasso with logarithmic penalty
AdaptiveGraphicalLasso(warm_start=True,
penalty=LogSumPenalty(alpha=1.0, eps=1e-10),
n_reweights=n_reweights,
tol=models_tol),
# Adaptive Graphical Lasso with L0.5 penalty
AdaptiveGraphicalLasso(warm_start=True,
penalty=L0_5(alpha=1.0),
n_reweights=n_reweights,
tol=models_tol),
]
Compute regularization paths#
nmse_results = {penalty: [] for penalty in penalties}
f1_results = {penalty: [] for penalty in penalties}
# Fit models across regularization path
for i, (penalty, model) in enumerate(zip(penalties, models)):
print(f"Fitting {penalty} penalty across {len(alphas)} regularization values...")
for alpha_idx, alpha in enumerate(alphas):
print(
f" alpha {alpha_idx+1}/{len(alphas)}: "
f"lambda/lambda_max = {alpha/alpha_max:.1e}",
end="")
model.alpha = alpha
model.fit(S, mode='precomputed')
Theta_est = model.precision_
nmse = norm(Theta_est - Theta_true)**2 / norm(Theta_true)**2
f1_val = f1_score(Theta_est.flatten() != 0., Theta_true.flatten() != 0.)
nmse_results[penalty].append(nmse)
f1_results[penalty].append(f1_val)
print(f"NMSE: {nmse:.3f}, F1: {f1_val:.3f}")
print(f"{penalty} penalty complete!\n")
Fitting L1 penalty across 10 regularization values...
alpha 1/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e+00NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.058
alpha 2/10: lambda/lambda_max = 3.6e-01NMSE: 0.674, F1: 0.123
alpha 3/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.3e-01NMSE: 0.606, F1: 0.330
alpha 4/10: lambda/lambda_max = 4.6e-02NMSE: 0.447, F1: 0.519
alpha 5/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.7e-02NMSE: 0.255, F1: 0.582
alpha 6/10: lambda/lambda_max = 6.0e-03NMSE: 0.108, F1: 0.573
alpha 7/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.2e-03NMSE: 0.046, F1: 0.541
alpha 8/10: lambda/lambda_max = 7.7e-04NMSE: 0.042, F1: 0.516
alpha 9/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.8e-04NMSE: 0.059, F1: 0.507
alpha 10/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e-04NMSE: 0.073, F1: 0.505
L1 penalty complete!
Fitting Log penalty across 10 regularization values...
alpha 1/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e+00NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.058
alpha 2/10: lambda/lambda_max = 3.6e-01NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.058
alpha 3/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.3e-01NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.058
alpha 4/10: lambda/lambda_max = 4.6e-02NMSE: 0.676, F1: 0.073
alpha 5/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.7e-02NMSE: 0.569, F1: 0.220
alpha 6/10: lambda/lambda_max = 6.0e-03NMSE: 0.355, F1: 0.485
alpha 7/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.2e-03NMSE: 0.133, F1: 0.724
alpha 8/10: lambda/lambda_max = 7.7e-04NMSE: 0.043, F1: 0.810
alpha 9/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.8e-04NMSE: 0.024, F1: 0.750
alpha 10/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e-04NMSE: 0.039, F1: 0.640
Log penalty complete!
Fitting L0.5 penalty across 10 regularization values...
alpha 1/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e+00NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.058
alpha 2/10: lambda/lambda_max = 3.6e-01NMSE: 0.682, F1: 0.059
alpha 3/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.3e-01NMSE: 0.644, F1: 0.142
alpha 4/10: lambda/lambda_max = 4.6e-02NMSE: 0.494, F1: 0.373
alpha 5/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.7e-02NMSE: 0.270, F1: 0.615
alpha 6/10: lambda/lambda_max = 6.0e-03NMSE: 0.095, F1: 0.726
alpha 7/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.2e-03NMSE: 0.034, F1: 0.685
alpha 8/10: lambda/lambda_max = 7.7e-04NMSE: 0.035, F1: 0.603
alpha 9/10: lambda/lambda_max = 2.8e-04NMSE: 0.055, F1: 0.547
alpha 10/10: lambda/lambda_max = 1.0e-04NMSE: 0.072, F1: 0.522
L0.5 penalty complete!
Plot results#
fig, axarr = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, figsize=([6.11, 3.91]),
layout="constrained")
cmap = plt.get_cmap("tab10")
for i, penalty in enumerate(penalties):
for j, ax in enumerate(axarr):
if j == 0:
metric = nmse_results
best_idx = np.argmin(metric[penalty])
ystop = np.min(metric[penalty])
else:
metric = f1_results
best_idx = np.argmax(metric[penalty])
ystop = np.max(metric[penalty])
ax.semilogx(alphas/alpha_max,
metric[penalty],
color=cmap(i),
linewidth=2.,
label=penalty)
ax.vlines(
x=alphas[best_idx] / alphas[0],
ymin=0,
ymax=ystop,
linestyle='--',
color=cmap(i))
line = ax.plot(
[alphas[best_idx] / alphas[0]],
0,
clip_on=False,
marker='X',
color=cmap(i),
markersize=12)
ax.grid(which='both', alpha=0.9)
axarr[0].legend(fontsize=14)
axarr[0].set_title(f"{p=},{n=}", fontsize=18)
axarr[0].set_ylabel("NMSE", fontsize=18)
axarr[1].set_ylabel("F1 score", fontsize=18)
_ = axarr[1].set_xlabel(r"$\lambda / \lambda_\mathrm{{max}}$", fontsize=18)
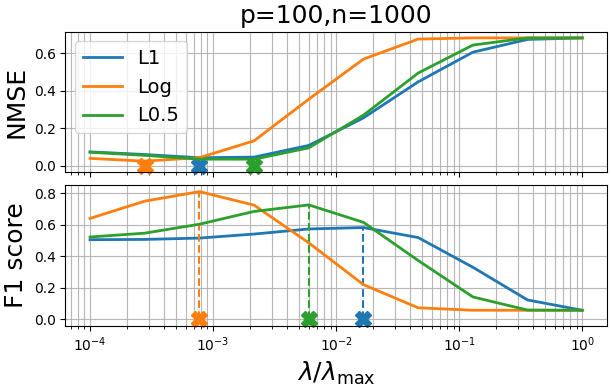
Results summary#
print("Performance at optimal regularization:")
print("-" * 50)
for penalty in penalties:
best_nmse = min(nmse_results[penalty])
best_f1 = max(f1_results[penalty])
print(f"{penalty:>4}: NMSE = {best_nmse:.3f}, F1 = {best_f1:.3f}")
Performance at optimal regularization:
--------------------------------------------------
L1: NMSE = 0.042, F1 = 0.582
Log: NMSE = 0.024, F1 = 0.810
L0.5: NMSE = 0.034, F1 = 0.726
Metrics explanation:
NMSE (Normalized Mean Square Error): Measures reconstruction accuracy of the precision matrix. Lower values = better reconstruction.
F1 Score: Measures sparsity pattern recovery (correctly identifying which entries are zero/non-zero). Higher values = better sparsity.
Key finding: Non-convex penalties achieve significantly better sparsity recovery (F1 score) while maintaining competitive reconstruction accuracy (NMSE).
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 39.915 seconds)